MADM™
Mobile Anesthesia Delivery Module
Military, humanitarian and emergency medical units are modernizing for large scale combat operations (LSCO), multi-domain operations (MDO), disaster relief, mass casualty and other emergency scenarios.
The Challenge
Meeting the Challenge
MADM™ is an inline gas anesthesia vaporizer that can be hand-carried to safely and accurately deliver gas anesthesia – anywhere your mission takes you. MADM™ automatically adapts its operation to the type of ventilator it is connected to.
Pair with MOVES® SLC™ and its proprietary circle-circuit ventilator for a compact, rapid-setup solution with efficient gas anesthesia use, NATO litter compatibility, and no compressed oxygen requirement.
MADM™ is ready for these challenges – today.
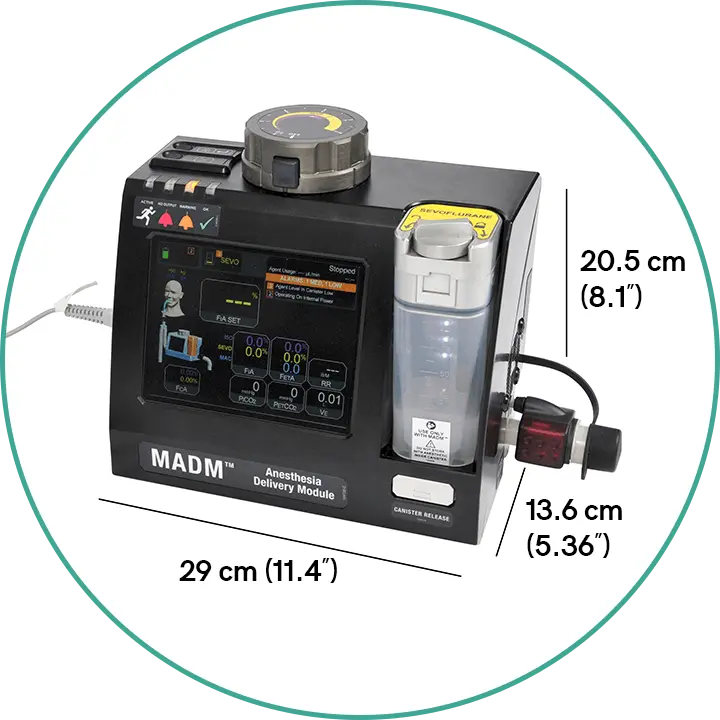

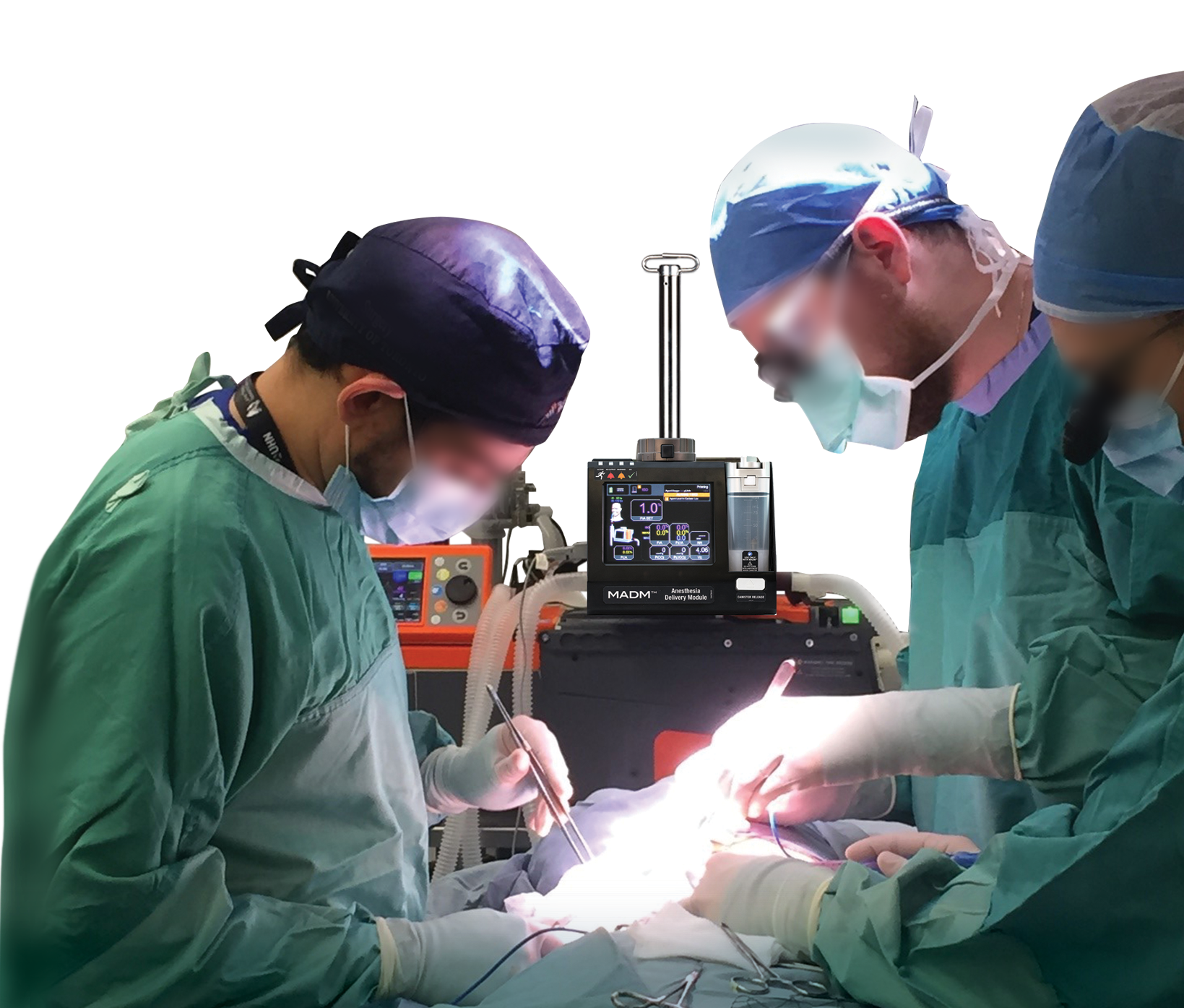
Versatile and Portable Design
The lightweight and compact design of MADM™ makes it ideal in more challenging environments such as field hospitals and forward-deployed surgical operations. MADM™ is quick to set up, easy to use, and has a small footprint – exactly what is required when time and space are at a premium, and mobility is required.
Accurate and Economical Anesthesia Delivery
MADM™ is very economical in its consumption of isoflurane and sevoflurane liquid anesthetic, and automatically adapts its operation to the type of ventilator it is connected to. In a circle-circuit configuration, MADM™ automatically reduces its vaporization rate to compensate for unused anesthetic returning from the patient, resulting in a substantial reduction in liquid anesthetic consumption.
More Functionality
MADM™ delivers accurate and consistent gas anesthesia concentrations over a broad operating temperature range.
MADM™ also provides embedded respiratory gas monitoring capability not typically found in deployable anesthesia equipment, giving anesthesia providers vital information such as inspired and end-tidal CO2 and anesthetic agent concentrations and minimum alveolar concentration (MAC).
Built for Extreme Conditions
MADM™ has undergone real and simulated life-cycle testing to confirm reliability in various extreme use environments. It has been evaluated for field use by the United States Army Aeromedical Research Laboratory (USAARL) and Air Force Medical Evaluation Support Activity (AFMESA). MADM™ functionality has been tested to confirm it meets the relevant FDA and international standards for electronic medical devices for its specific functionality.


